Introduction
HaloENGINE is a Java-based component exposes a web service to the HaloCAD for PLM and the HaloCORE SAP Add-On. Both HaloCORE and HaloCAD security solutions use it as a common component. Microsoft Purview Information Protection (MPIP) is seamlessly integrated into HaloCORE and HaloCAD solutions to ensure the protection of your sensitive documents.
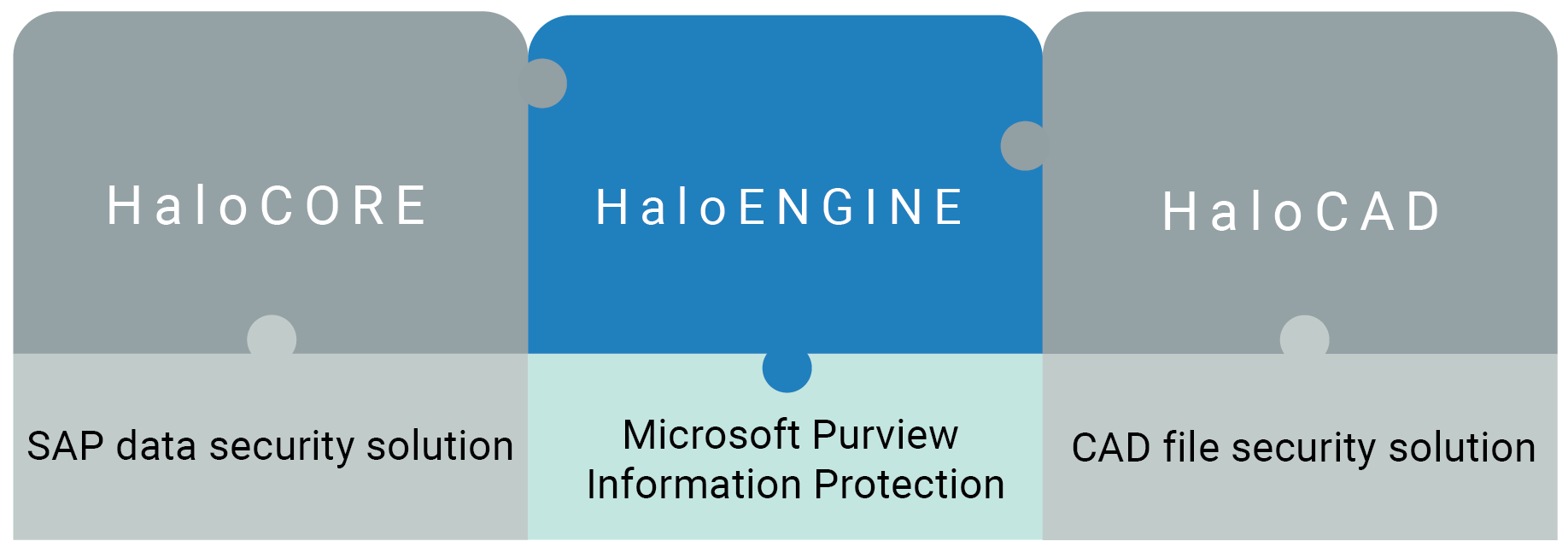
HaloENGINE as a common component
HaloENGINE Features
-
Business logic: All business logic decisions are handled by this classification engine.
-
Logging the audit logs: Captures any file upload or download regardless of file protection.
-
Supports SIEM solutions such as Microsoft Azure Sentinel, Splunk, RSA, and others.
-
Halochain: Investigates the log file.
-
Dashboard: Displays important performance indicators and metrics, providing an overview of the company's data upload and download events.
About HaloENGINE
HaloENGINE is a Java-based component that classifies data into various groups based on defined parameters such as metadata. Any organization's business logic will be housed in this classification engine.
What is HaloENGINE Service?
The HaloENGINE Service is a Windows service that connects to the HaloENGINE over TCP/IP. It is the only component that directly communicates with the Azure Right Management Service (Azure RMS) to obtain the MPIP label required to protect a file. It actively listens to HaloENGINE decisions and encrypts and decrypts files based on them.
The rules are defined by the administrator in HaloENGINE based on the requirements of the organization, and the HaloENGINE Service then executes them to encrypt and decrypt files. The processing of PLM CAD and SAP data in HaloCORE and HaloCAD solutions relies heavily on the rules established in HaloENGINE.
About this Manual
This manual will guide you through the installation and configuration of the following components:
-
HaloENGINE
-
HaloENGINE Service
-
HaloENGINE API
This is the primary document that administrators must read before installing HaloCORE or HaloCAD. Following that, read the installation and operation manuals.
General Concepts of Classification
Sensitive Data Classification: This is the process of identifying and categorizing all the data in an organization depending on its sensitivity. When a systematic method of data classification is used, sensitive information is adequately protected and made accessible to those who need it. For example, more sensitive data, such as financial information, might be categorized in such a way that disclosure carries a higher risk. General information, such as those utilized for marketing, would be categorized as a lower risk. A higher level of protection is necessary for data identified as having a higher risk, whereas lower-risk data may need proportionately less protection. A data classification schema describes a specific approach to determining data classification levels.
Levels of Sensitive Data
Depending on sensitivity, data is typically categorized into several kinds.
-
Public: low data sensitivity
-
Internal: moderate data sensitivity
-
Confidential: high data sensitivity
You can take suitable action on the appropriate content in this situation with the use of Microsoft Purview's sensitivity labels. Sensitivity labels allow you to identify the level of sensitivity of data across your organization and impose protective settings that are appropriate for the sensitivity of that data.
How are labels created?
Through the Microsoft Purview portal, you can administer how labels are published to your users. For more details, please refer to Microsoft online documentation.
Classification Scheme
It takes meticulous planning and preparation to define a classification scheme for an organization and set information types and labels. Each organization is unique, and there is no one-size-fits-all data protection rules. You could design your classification scheme based on the business context. Throughout this chapter, a basic-level scenario is used to demonstrate the configuration classification engine. Classifying data can be done in various ways, but most businesses prefer to use a three-level classification schema: Public, Internal, and confidential.
Best Practices
Consider the following suggestions when creating classification labels:
-
Use existing classification schema (if any).
-
Use sub-labels for key departments. Some departments will have specific needs that require specific labels.
-
Use meaningful label names, it is recommended not acronyms as label names. Consider names as follows for property Sensitivity.
-
Personal - Non-business data, for personal use only.
-
Public - Data that is specifically prepared for public consumption such as marketing material or press announcements.
-
Confidential - Sensitive business data that could cause damage to the business if shared with unauthorized people. Examples include contracts, security reports, and sales account data.
-
Secret - Very sensitive business data that would cause damage to the business if it were shared with unauthorized people. Examples include customer information, contract letters, and pre-announced financial reports.
-
Classification Rule Engine
This is where HaloENGINE's business logic resides. It comprises the following:
-
Classification Schema - Defines which data categories will be used to categorize the organization's data.
-
Classification Rules - Rules are defined based on metadata and action rules to determine whether to block, label, protect, or decrypt a file.
Use the table below to decide how you want to deploy the features.
|
Actions |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Monitor |
File uploads and downloads are audited. |
|
Block |
File uploads and downloads are blocked. |
|
Label/Protect |
File uploads and downloads are classified. Using appropriate MPIP labels, classification labels are embedded in the file metadata. |
|
Notify |
Notifies about actions performed via SAP front-end. Please note that ‘Notify’ is not supported by non-SAP clients. |
Action description
Quick Start Installation Summary
The following visual illustrates the high-level concept of configuring HaloENGINE in HaloCORE and HaloCAD.
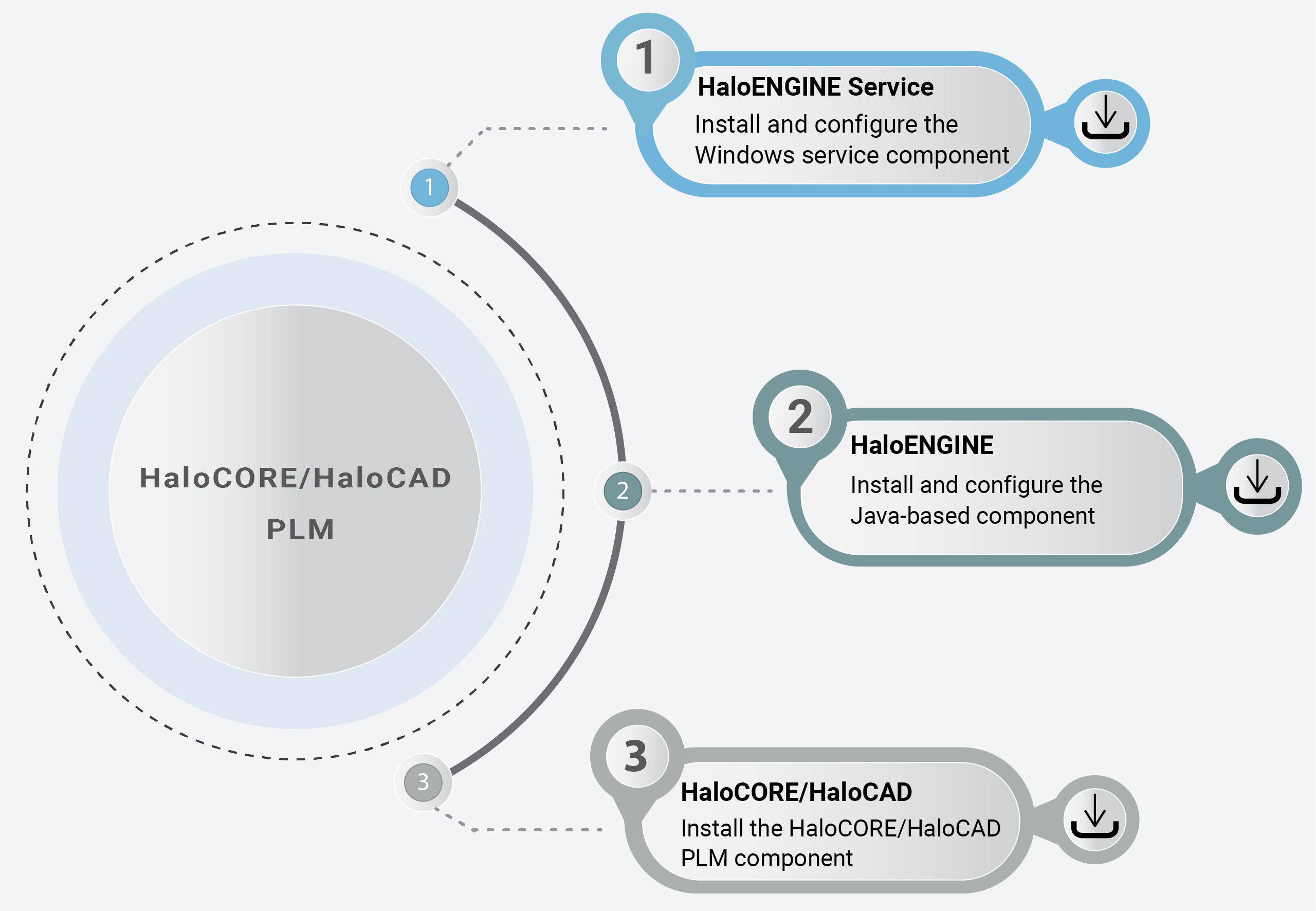
Quick start installation steps
Reference Manuals
The table below describes where to obtain information.
|
Component |
Refer to |
|---|---|
|
Step 1 – Install and configure the Windows Service component. |
Refer to the section “Installing the HaloENGINE Service”. |
|
Step 2 – Set up and configure the Java component. |
Refer to the section “Installing the HaloENGINE”. |
|
Step 3 – Install HaloCORE or HaloCAD. |
Refer to the HaloCORE or HaloCAD manual. |
Reference Manuals
